The winter period is quite uncomfortable for mainly truck drivers since they have to put their judgments to the test. The drivers are given the responsibility of taking care of their equipment for them to be able to efficiently, safely, and economically operate at extremely low temperatures. The cold weather is the primary contributor for fast wear and tear of some components, making them susceptible to damage; in fact, all it takes is a brief lapse in maintenance for the driver to end up abandoned on the road. Doing vehicle care for the winter is not just about enjoying a smooth ride; it is by far, about ensuring a commercial vehicle survives the extreme mechanical challenges it can go through.
Freezing weather is like an episode of kung fu: the enemies are full of action; the batteries fade life; fluid levels are turned to crystal and tire pressure disappears. Even heating systems are forced to work overtime. In the absence of preventive maintenance, winter driving can quickly translate into dead batteries, tire blowouts, heating failures, and unplanned roadside assistance calls that in turn disrupt schedules and inflate operating costs.
This guide dwells on four main targets in the winter maintenance for truck drivers as follows: Batteries, fluids, heating, and tires. It gives the details of the minor checks that matter most, states the reason why they become critical in cold weather, and illustrates how the harsh winter conditions make the situation with risks in the vehicle systems worse.
Establishing the Need for Truck Driver Winter Maintenance
Batteries, Fluids, Heating, and Tires
Unlike passenger vehicles that are fitted and cover a certain mileage, trucks are usually on the ground a lot longer, and they tend to idle overnight or run the course of a single route with varying temperatures. Cold weather, therefore, is not merely a mechanical fault resulting in a system slowdown — this is a condition where the margin for error is drastically reduced.
Winter car preparation for commercial vehicles revolves around:
- Eliminating cold-type failures before they occur
- Retaining steering and self-assurance in winter driving
- Maintaining the operational state of trucks in out-of-the-way areas and avoiding car trouble
- Reducing auto repair costs that result from sudden failures
These principles are not casual habits but structured car care tips adapted specifically for winter operation of commercial trucks. Winter maintenance is not reckless car maintenance. It is structured preemptive maintenance built to ensure that the truck goes without functional weaknesses that the cold weather has exposed.This approach aligns with winter vehicle safety guidance published by the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), which highlights battery performance, coolant condition, tire pressure, and heating system reliability as critical winter preparation factors for commercial vehicles.Source: https://www.nhtsa.gov/winter-driving-tips
Battery Health: The Weakest Link in Cold Weather Systems
The low temperatures greatly reduce battery capacity. A battery that progressed successfully in a warm environment can suddenly expire in harsh frost overnight.
Cold Temperatures Are to Blame for Defective Batteries
- Cold weather processes happen slower
- The engine oil is thick so it has to be cold to start
- Prolonged sleep reduces battery lifespan
Defective batteries are, by far, the major cause of road assistance during the winter season, mostly happening without prior warning.
Winter Battery Health Checklist
- Test battery voltage and load capacity
- Inspect terminals for corrosion and loose connections
- Verify charging system output
- Replace aging batteries before winter peak demand
Neglecting the battery is one of the basic reasons why people have winter car problems and they miss scheduled deliveries.
Battery Vitality Under Winter Load and Fluctuating Temperatures
Battery health in winter is often misunderstood as a cold-only issue, while in reality it is the result of cumulative stress across seasons. Extremely hot days in the sum… inter speed up internal battery rotting, liquefy the electrolyte, and reduce the size of plates. Upon the onset of the winter season, those concealed vulnerabilities break out right away. A battery that went through hot months without any signs may quickly fail or just stop working when the temperature goes down.
Cold weather not only affects battery functionality but also increases the electrical demand. Starting motors require more juice due to the thickened engine oil, heaters and defrosters consume additional electrical load, the battery is drained more quickly with a longer period of idle times. Without appropriate battery health checks such as tests for state-of-charge, trucks may not be properly serviced in remote areas and face no-start problems.
Efficient maintenance of the car in the cold season as far as battery functioning is concerned includes load testing which is more enlightening than just attempting to guess the cold-c rating from the voltage reading. A battery may seem to have adequate voltage while it is in reality insufficient for cold cranking. Terminal cleanliness is equally important, as corrosion adds resistance exactly when each amp matters most. Inspecting charging system output to make sure that the alternator works is critical as a compensator for the higher electrical load of winter.
Battery health issues due to lack of maintenance can result in unplanned roadside emergencies and downtime. Changing old batteries for new ones is, in fact, risk reduction at the small cost of the lost asset. Torpedo trucks that are left work or go in the north are very needed to see batteries as temporary safety devices not assets due for long service.
The winter season reveals the hidden damage caused by extreme heat. Those who comprehend the connection between seasonal maintenance understand that by preventing seasonal problems drivers and fleet managers help cut down on such issues during winters when the temperature drops and the weather becomes bleak.
Fluids: Cold Weather Changes the Rules
Fluid levels and fluid condition are central to winter car prep. Low temperatures alter viscosity, restrict flow, and increase the risk of freezing, pressure buildup, and internal damage.
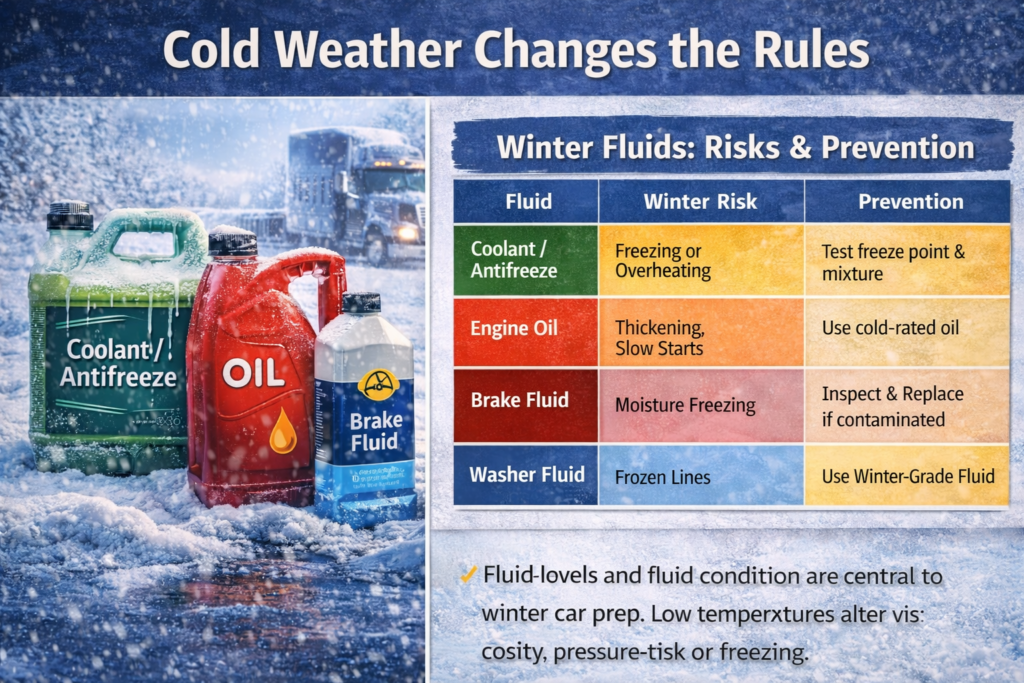
Flush and Replace Critical Fluids
- Coolant fluid / antifreeze – prevents freezing and overheating
- Engine oil – cold-rated oil improves cold starts and reduces wear
- Brake fluid – moisture contamination worsens in winter
- Washer fluid – winter-grade fluid prevents frozen lines
Using incorrect fluids or neglecting fluid levels brings about engine damage, braking issues, visibility loss, and end up with costly repairs.
The Ultimate Winter Car Care Guide | How to Winterize Your Vehicle for Safe and Smooth Driving
Risks and Prevention of Winter Fluids
| Fluid Type | Winter Risk | Preventive Action |
| Coolant / Antifreeze | Freezing or overheating | Test freeze point and mixture |
| Engine Oil | Thickening, slow starts | Use cold-weather rated oil |
| Brake Fluid | Moisture freezing | Inspect and replace if contaminated |
| Washer Fluid | Frozen lines | Use winter-grade fluid |
Well-managed fluids are in fact, the foundation of winter maintenance so always incorporate them in your vehicle check-up routine.
Truck Car Heating, Antifreeze Fluid, and Thermal Equilibrium in Winter Operations
The heating system of a truck not only provides comfort for the cabin but also is the core element of safety, visibility, and engine thermal stability. A properly functioning heating system is essential to driver comfort and decision making during the long cold winter shifts for the driver is often affected by the defrosting of the windshield. Failure in heating is usually a result of neglected coolant fluid issues but not blower motors or valves.
Coolant fluid has two main features: in winter, it prevents freezing and all year long, it is in charge of heat transfer. Low antifreeze concentration or expired coolant inhibit both functions. While winter is the risk factor standing for the freez… pr the year pulling apart of the antifreeze no corrosion will happen in the heat season. Before the cold season begins, the system of the heating radiator might be already competing with a battle of function.
Essential tips for winter vehicle maintenance include testing ant… and hoses, checking circuit paths, and verifying proper circulation through the heater core. Often, a cooler than average cabin in winter suggested a separate problem of restricted flow or air pockets in the cooling system. Ignoring such signs the engine may overheat even in low temperatures work during heavy loads.
Equal heat regulation relies on preventative maintenance more than based on repairing things after the problem occurs. Heating systems that run well have the advantage of boosting driver endurance, keeping visibility safe, and making it stable engine temperatures. The trucks without quality heating staff suffer from driver problems of fatigue and distraction therefore increasing the risk of operations.
Winter maintenance is not only for surviving cold starts; winter management encompasses system balance by controlling heat on the ones that were stressed by extreme heat months before. The management of coolant fluid and the operation of a heater form a chain of safety driving equipment and the driver through the winter season protegido.
Heating Systems: Safety, Not Comfort
Car heating in trucks is not only about driver comfort but also safety. If the heating system fails, the bus fogged up, the driver gets sleepy, and visibility got worse during snow, sleet, and night driving.

Heating System Checks for Winter
- Heater core performance
- Blower motor operation
- Defrost response speed
- Cabin airflow consistency
A malfunctioning heating system can quickly escalate into visibility loss, fatigue, and unsafe winter driving conditions.
Tires: Pressure, Traction, and Structural Risk
Cold weather reduces tire pressure naturally. Underinflated tires increase rolling resistance, reduce traction, and dramatically increase the likelihood of tire blowouts.
Winter Tire Inspection Essentials
- Check tire pressure frequently
- Inspect tread depth and wear patterns
- Examine the sidewalls for cracking or bulging
- Verify if the tires meet the winter rating requirement
Tire Risks in Winter Conditions
| Issue | Cold Weather Effect | Resulting Risk |
| Low tire pressure | Reduced traction | Skidding and loss of control |
| Worn tread | Poor grip on snow | Increased stopping distance |
| Sidewall damage | Cold-induced cracking | Sudden tire blowouts |
Donning the habit of regular tire inspection is one of the best ways to prevent winter roadside emergencies.
Preventative Maintenance vs Emergency Repairs
Preventative maintenance is always lower than emergency car repair during the wintertime. Cold-related failures usually involve:
- Longer response time
- Higher towing and labor cost
- Limited repair access in remote areas
Though hot weather can overworked systems make it, cold weather is more strict because failures can occur suddenly and without any notice.
Proper maintenance is the key to less downtime, keeping the schedule on target, and avoiding roadside emergencies.
The Conclusion: Winter Maintenance Is an Operational Discipline
Winter maintenance is not merely seasonal advice – it is a discipline in operations. The battery’s health, the fluid coolant management, the car’s heating reliability, and the tire inspection collectively decide if a truck will live through the winter or become a liability.
Prepared trucks keep moving. Unprepared trucks stop.
Winter car prep turns unfavorable cold weather into manageable operating conditions. For professional drivers, preventative maintenance is not a choice; it is the difference between control and crisis when the winter road tests both the machine and the judgment.
Winter Maintenance for Truck Drivers: Mini FAQ
Why is it more common to have vehicle breakdowns during winter than in the other seasons?
Winter weather decreases system tolerance. The battery production goes down, fluids get thick or they freeze, the tire pressure decreases, and the heating systems work under constant load. All of these stresses working together unmask the weaknesses that, in warmer weather, could remain invisible.
How many times should I check the battery according to its status in winter?
Testing battery conditions should be the first thing to do before winter and regular testing should be performed during the season, especially for trucks that travel in isolated or cold areas. A load test is more effective rather than solely relying on a voltage check in the cold season.
Is it only the antifreezing that is saved by using antifreeze?
Not at all. Coolant fluid and antifreeze are also responsible for the maintenance of the engine’s temperature and for the inner components from getting rusted. If there is a wrong concentration of the antifreeze, the engine can overheat while still in freezing conditions, especially if it has to bear intensive load.
Why are tire blowouts more likely in winter?
Low temperatures cause a drop in tire pressure and increase the side sill of the tire. The risk of sudden burst of tires is raised by the combination of these factors with the worn-out tread, unnoticed damage, and the long hauls, or driving on icy surfaces.
Can preventive maintenance actions really decrease the time of winter breakdowns?
Yes. Preventive measures drastically cut the number of times very often they have to call roadside assistance, have to do emergency repairs on vehicles, and have late deliveries. Winter maintenance is about keeping the system balanced rather than dealing with issues when they happen.




